Difference between revisions of "Fog Computing"
ArvindIOTF (talk | contribs) m (→Fog vs Edge) |
ArvindIOTF (talk | contribs) m (→Open Fog Consortium) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
:Cloud-to-Thing continuum of services: Enable services and applications to be distributed closer to Things, and anywhere along the continuum between Cloud and Things | :Cloud-to-Thing continuum of services: Enable services and applications to be distributed closer to Things, and anywhere along the continuum between Cloud and Things | ||
:System-level: Extend from the Things, over the network edges, through the Cloud, and across multiple protocol layers – not just radio systems, not just a specific protocol layer, not just at one part of an end-to-end system, but a system spanning between the Things and the Cloud | :System-level: Extend from the Things, over the network edges, through the Cloud, and across multiple protocol layers – not just radio systems, not just a specific protocol layer, not just at one part of an end-to-end system, but a system spanning between the Things and the Cloud | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[https://www.iiconsortium.org/wc-technology.htm The Industrial Internet Consortium] has taken over from the openFog Consortium and has a reference document. [https://www.iiconsortium.org/pdf/Introduction_to_Edge_Computing_in_IIoT_2018-06-18.pdf Introduction to Edge Computing in IIoT] | ||
{| | {| | ||
Revision as of 01:52, 6 November 2019
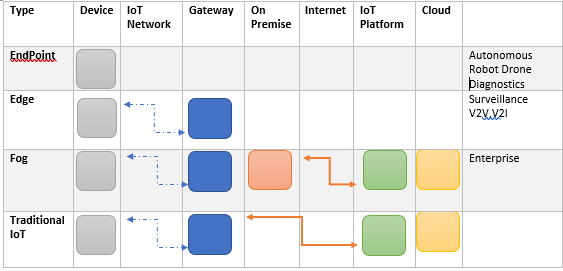
Fog computing was coined by CISCO and envisages multiple compute points in an IOT network. Instead of the cloud being the sole compute engine gateways and other network infrastructure may have the resources ( being full fledged Linux devices) to pre process the data before sending to back end applications or sometime even processing it locally. Fog is different from the old Distributed Computing in the sense that many different compute engines of different capacity collaborate in near real time ( multiple gateway, On premise and cloud ). A common usage is in network surveillance and malware detection
Edge computing by contrast implies only one local compute point (the endpoint) which is connected but did not use of cloud or on premises resources in responding to an event. Local inference in terms of AI
Fog vs Edge
Many use the terms fog computing and edge computing (or edge processing) interchangeably. However there is a subtle but important difference as special purpose chips running AI/ML at edge start coming into use.
| Quote | Source |
|---|---|
| The key difference between the two architectures is exactly where that intelligence and computing power is placed,” he said. According to Newton:
Fog computing pushes intelligence down to the local area network level of network architecture, processing data in a fog node or IoT gateway. Edge computing pushes the intelligence, processing power and communication capabilities of an edge gateway or appliance directly into devices like programmable automation controllers (PACs). |
---What is edge computing and how it’s changing the network |
Open Fog Consortium
- OpenFog Consortium
Fog computing is a system-level horizontal architecture that distributes resources and services of computing, storage, control and networking anywhere along the continuum from Cloud to Things. It is a:
- Horizontal architecture: Support multiple industry verticals and application domains, delivering intelligence and services to users and business
- Cloud-to-Thing continuum of services: Enable services and applications to be distributed closer to Things, and anywhere along the continuum between Cloud and Things
- System-level: Extend from the Things, over the network edges, through the Cloud, and across multiple protocol layers – not just radio systems, not just a specific protocol layer, not just at one part of an end-to-end system, but a system spanning between the Things and the Cloud
- The Industrial Internet Consortium has taken over from the openFog Consortium and has a reference document. Introduction to Edge Computing in IIoT